Ceiling lights
Top selling products in the category
There are 11 products.
5.36 €
5.36 € without VAT
Waterproof LED mini ceiling light 3W, stainless steel
In stock
Mini waterproof LED garden lamp with a power of 3W. Diameter 48mm. Stainless steel with IP68 protection.
31.98 €
31.98 € without VAT
Waterproof LED mini ceiling light 1W, stainless steel
In stock
Mini waterproof LED garden light with 1W output. Diameter 20mm. Stainless steel with IP67 protection.
10.49 €
10.49 € without VAT
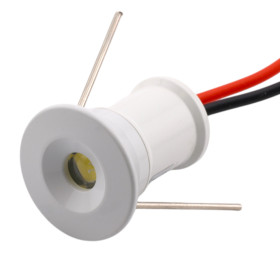
LED mini ceiling light 1W, white
In stock
Mini LED furniture luminaire with power 1W. Aluminum in white anodized finish.
5.03 €
5.03 € without VAT
LED mini ceiling light 1W, black
In stock
Mini LED furniture luminaire with power 1W. Aluminium in black anodised finish.
5.03 €
5.03 € without VAT
LED mini ceiling light 1W, silver
In stock
Mini LED furniture luminaire with power 1W. Aluminium in silver anodised finish.
5.03 €
5.03 € without VAT
LED ceiling light for plasterboard, circular, 6W, 120°
In stock at supplier
5.90 €
5.90 € without VAT
4.73 €
4.73 € without VAT
LED spot light for plasterboard Cree 7W
In stock at supplier
15.56 €
15.56 € without VAT
13.39 €
13.39 € without VAT
9.89 €
9.89 € without VAT